The Institute for Sustainable Infrastructure (ISI) announced that the Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) of North Central Texas has earned the Envision™ sustainable infrastructure rating system’s Silver award for their Line J, Section 1 Pipeline project. The pipeline was designed by Freese and Nichols, Inc., a charter member of ISI. The Tarrant Regional Water District accepted the award from ISI President and CEO, William Bertera, during the Board of Directors Meeting on September 23, 2014 at 9:00 am at the TRWD Administration, 800 East Northside Drive, Fort Worth, TX, 76102.
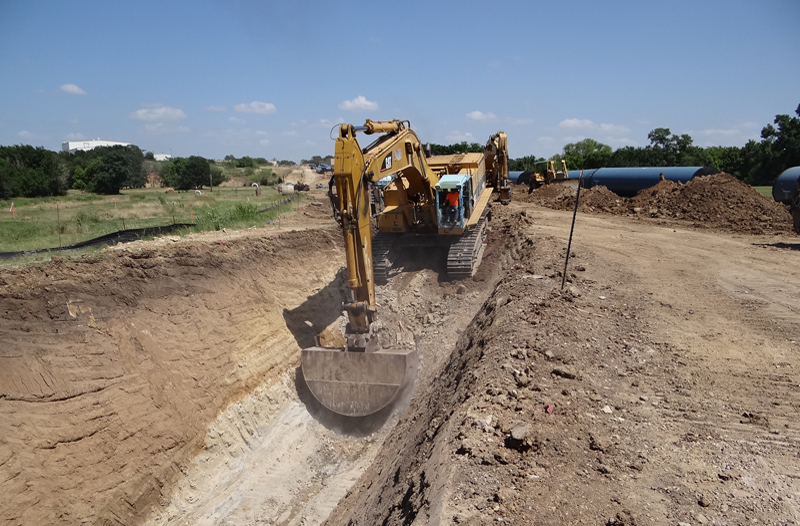
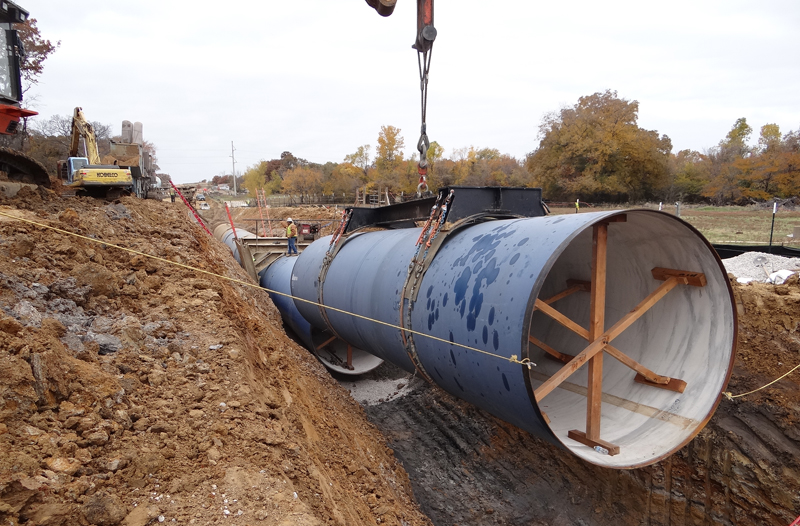
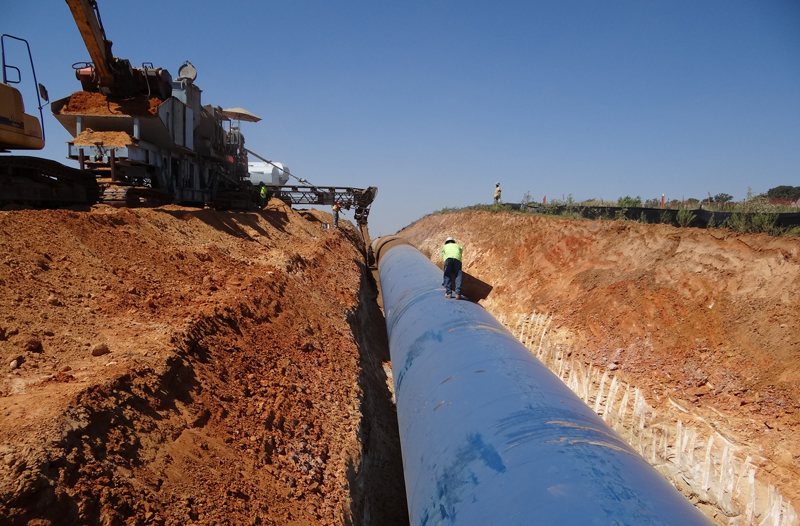
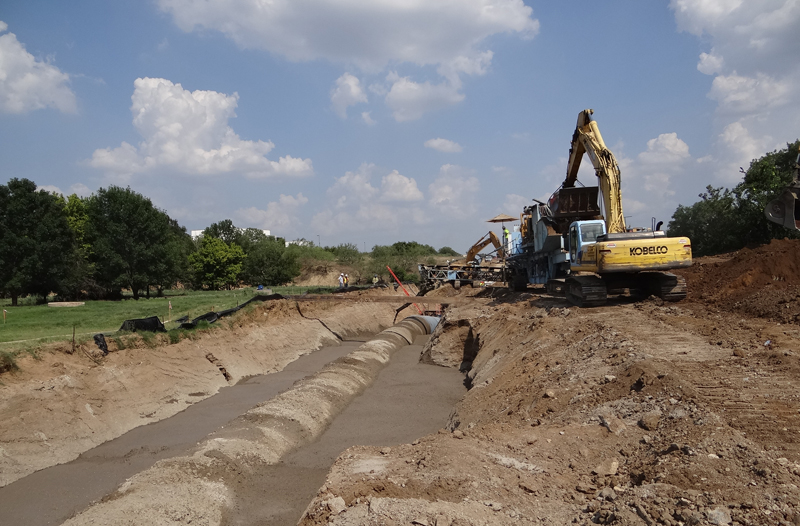
The Envision™ Silver award-winning project is a two mile, 108-inch diameter pipeline delivering water from the Kennedale Balancing Reservoir directly to the Arlington Outlet, dedicating a significant amount of water demand from the existing pipelines, and allowing the District to meet future demands at the Rolling Hills Water Treatment line, and BioPro Sewage Treatment further west. The water delivered to the Arlington Outlet can be either piped through the existing discharge facility, or go through to the new hydroelectric facility.
“The TRWD pipeline project received the ISI Envision™ Silver award because of its areas of high achievement in the quality of life for communities in the area that have experienced drought conditions, as well as the stimulation of sustainable growth and development due to increased water demands in one of the fastest growing communities in the U.S.”, said ISI President and CEO, William Bertera. “The TRWD has also provided effective leadership and commitment to begin and implement sustainable practices, and significant efforts have been undertaken by the District to put their commitment into action”, Bertera said.
Shelly Hattan, the Line J Project Engineer, said “TRWD is very proud of our achievement of infrastructure sustainability as recognized by the ISI Envision™ Silver award. This pipeline provides increased system reliability to area customers, and is designed to accommodate future water supplies in the area. The evaluation of this project by the industry’s leading sustainability rating system shows that TRWD is expanding our continued commitment to sustainable practices.” Learn more about this streamlined system of customer service and how it can benefit your own projects and company.
The Envision™ system measures sustainability in infrastructure projects through the measurement of five categories: Quality of Life (QL), Leadership (LD), Natural World (NW), Resource Allocation (RA), and Climate and Risk (CR) that contribute to overall credits for the positive social, economic, and environmental impacts in a community in the planning, design and construction of infrastructure projects. The highest-rated project categories that the TRWD Pipeline scored using the Envision™ rating system included.
Quality of Life (QL): The TRWD Pipeline project scored highly in the improvement of area communities’ quality of life. Water demands in Tarrant County are expected to double in the next 50 years, and area lakes have not been able to meet demands, leading to TRWD’s extensive water transmission system. The project improves the net quality of life for many of the communities served by TRWD by increasing their ability to transfer raw water to 1.9 million users.
It also stimulates sustainable growth and development through increased water availability, which increases the community attractiveness to new business and residents. By adding Line J, the efficiency and reliability of TRWD’s water transmission system increases while deferring the need for new water supplies and for more pipelines and pump stations. TRWD’s strategic water plans and operations align with the anticipated economic and development growth of TRWD’s service area.
Leadership (LD): TRWD began implementing sustainable practices prior to the project, and the evaluation and implementation of sustainable practices had been a priority since the beginning of the pipeline project. A Project Management Plan was prepared at the beginning of the project to establish goals, procedures, communication, controls, etc. The consultant team was led by Alan Hutson, P.E., ENV SP, for Freese and Nichols, and sustainability guidance was provided by Elizabeth Blackwelder, P.E., ENV SP, also from Freese and Nichols, which has 26 certified sustainability professionals.A Contractor Manager at Risk (CMAR) was brought in early on to help manage changing conditions, critical schedule, and experimental features of the project. In addition, two specific sustainability tasks were included in the project scope to evaluate complex design alternatives and enhance sustainable management of the project. The team met regularly to assess progress made, convey new data, identify issues, and discuss solutions.
Leadership in this context involves fostering collaboration and teamwork. Significant collaborative effort went into evaluating the use of trench excavated material for pipe embedment through the development of native CLSM. Having a CMAR in the project automatically incorporates a benefit/risk sharing component. For example, the CMAR was required to review and provide evaluation regarding construction cost throughout different phases of the project, identify potential bidders, create interest in the project amongst contractors and manufacturers, etc.
In implementing a sustainable design, the team applied the Envision™ Sustainable Infrastructure Rating System. They also involved civil engineering graduate students at the University of Texas at Arlington, who evaluated the use of native soils to produce controlled low-strength material (CLSM). Collaboration and design integration with the students produced exceptional social benefits.
Natural World (NW): To maintain wetland and surface water functions, hydraulic studies and geomorphology studies were performed at Village Creek to complete the pipeline crossing under the creek and the surface restoration design. Two ecosystem functions are maintained by the Line J pipeline. Hydrologic connections are maintained and enhanced by restoring all contours to existing pre-construction contours at creek crossings. Sediment transport functions are maintained by removing materials deposited in the bottom of the creeks which impede the natural flow of the water carrying sediment.
Also rated by the ISI Envision™ system were the Resource Allocation and Climate and Risk categories of the TRWD Pipeline project, along with the three previous categories. Highlights from these categories helped the project win with the Envision™ Silver award.
Resource Allocation (RA): The design of the Line J Pipeline incorporates several initiatives to reduce excavated materials taken off site. The excavated soils will be used as: pipe embedment, trench backfill, borrow material to grade properties adjacent to the pipeline, and Pipe Embedment.
The credit was exceeded by developing a method to design, field produce, and field install an embedment material produced with low quality trench excavated soils. This methodology is new to Texas.
Climate and Risk (CR): TRWD has worked towards addressing raising water demand in a responsible way for many years. To the District, this means operating safely, minimizing the adverse impact on the environment, building infrastructure as the service area needs it, and building trust with the customer communities. Their infrastructure system, which Line J is part of, is designed, operated, and maintained to be flexible and resilient to changing climate and social conditions.
For more information about the TRWD Pipeline Project, contact Shelly Hattan at: (817) 720-4256, or [email protected], or Chad Lorance, TRWD Communications Manager, at 817-335-2491 ext. 367, or [email protected].
For more information about Freese and Nichols, contact Lindsey Kubes at (817) 735-7320, [email protected].
For media information about the Institute for Sustainable Infrastructure (ISI), visit the website at www.sustainableinfrastructure.org, or contact Laura Bynum, ISI/APWA Media Relations Manager at 202.218.6736, or [email protected]
About TWRD:
For more than 80 years, the Tarrant Regional Water District has provided quality water to its customers, implemented vital flood control measures and created recreational opportunities for Tarrant County residents and communities. Led by a publicly elected five-member board, the Water District owns and operates four major reservoirs including Lake Bridgeport, Eagle Mountain Lake and the Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs. TRWD has also constructed more than 150 miles of water pipelines, 27 miles of floodway levees, more than 40 miles of Trinity River Trails and a 260 acre wetland water reuse project designed to increase future water supplies for the area. As one of the largest raw water suppliers in the state of Texas, TRWD provides water to more than 1.7 million people in the North Central Texas area. TRWD serves more than 30 wholesale customers including the cities of Fort Worth, Arlington, Mansfield and the Trinity River Authority. Operations span an 11-county area reaching from Jack County to Freestone County and include maintenance of dams at the Water District’s four reservoirs as well as the more than 150 miles of pipeline used for water transport.
About ISI Envision™:
Envision™ is the product of a joint collaboration between ISI, which was founded by three national engineering associations: American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), American Council of Engineering Companies (ACEC), and American Public Works Association (APWA), and the Zofnass Program for Sustainable Infrastructure at Harvard University Graduate School of Design. Information on all of ISI and Envision™ can be found on the ISI website, www.sustainableinfrastructure.org.
About Freese and Nichols, Inc.
Freese and Nichols is a full service professional consulting firm and the first engineering/architecture firm to receive the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award. With offices in Texas and North Carolina, Freese and Nichols provides services in engineering, architecture, environmental science, planning, construction services, energy and program management. A charter ISI member, Freese and Nichols has 26 certified sustainability professionals. For more information about Freese and Nichols, visit www.freese.com.











Join us now ZPH Workshop: #Sustainable #Infrastructure for #ClimateAction in-person & ZOOM https://t.co/fCjkr0Ykrh
About 2 years ago from Zofnass Program's Twitter